We are building a sports data network that disrupts the equilibrium.
Athlete data is harvested instead of rewarded. We are building a suite of apps to give athletes ownership and control over their data.
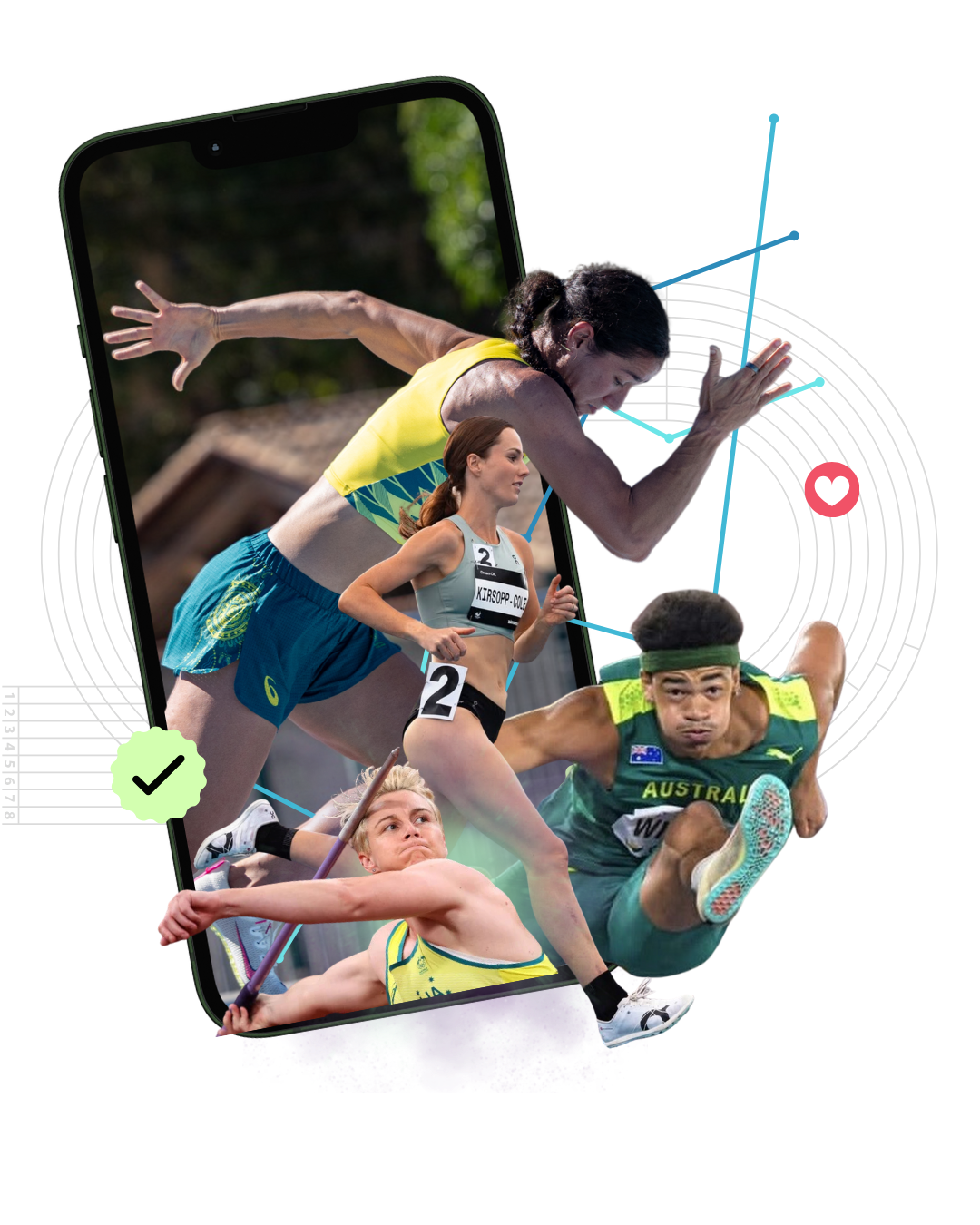

Our Mission
We build applications that solve real-world problems, return data ownership to users, and foster connected, empowered communities.
Users shouldn’t just interact with their data—they should own it. Our platform empowers individuals to contribute, control, and monetise their performance insights, engagement metrics, and digital content on their own terms.
Our Apps
What we have been working on

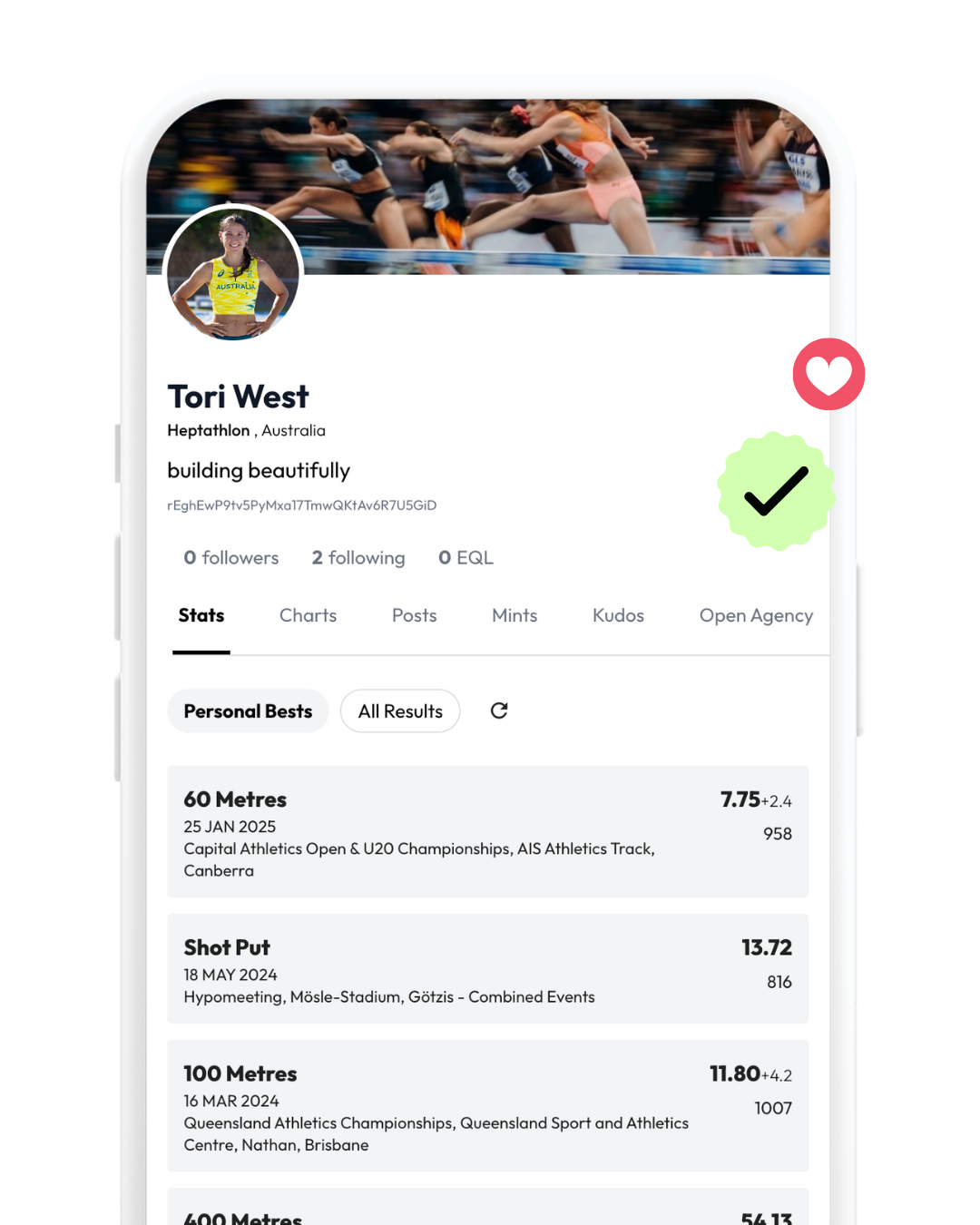
Digital Training Diary for athletes that put all athlete data in one place.
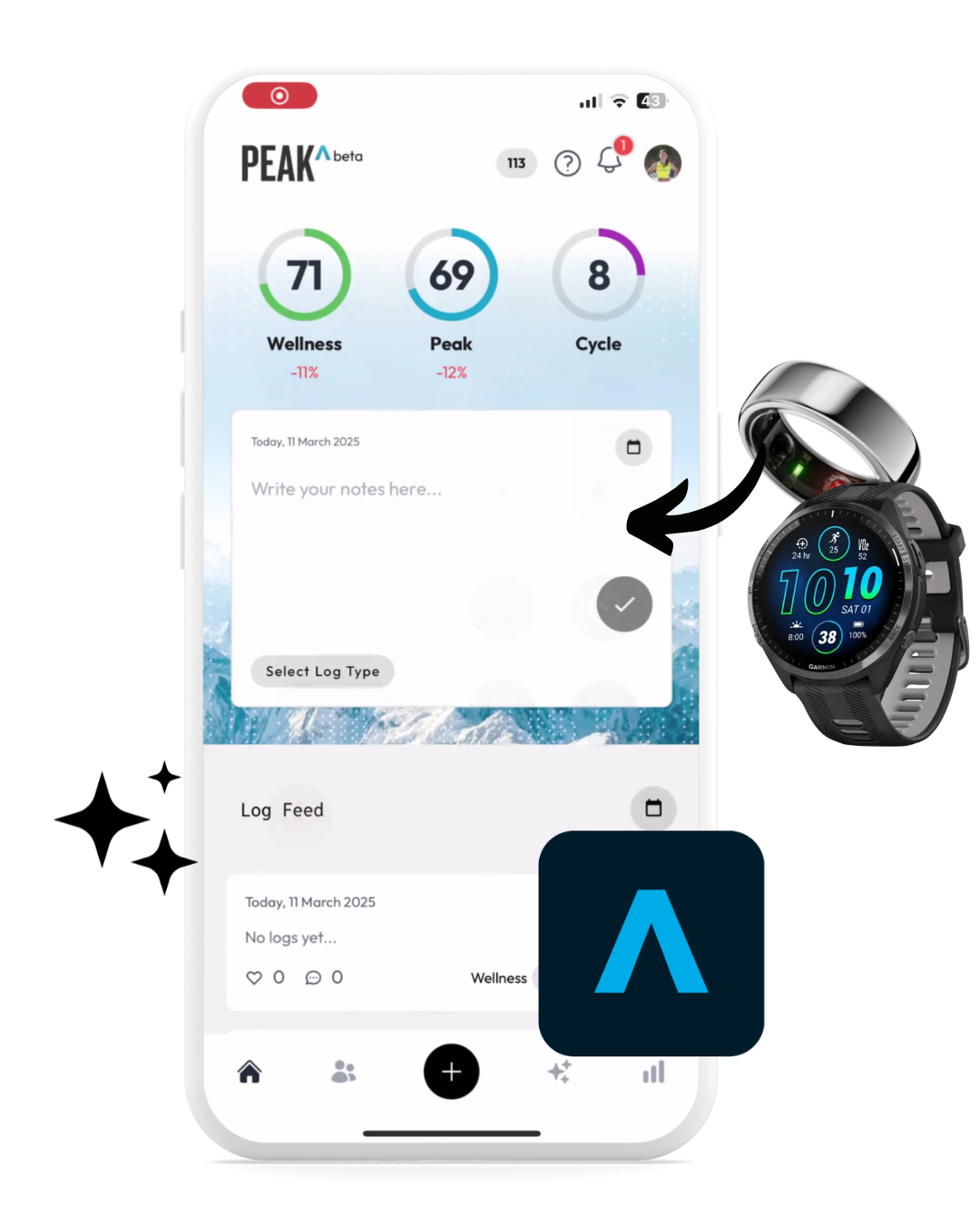

LinkedIn for Athletes and Data Marketplace for Brands & Agencies.
Full Stack Digital Development
We design and build customProgressive Web Applications (PWAs)
Tailored for Sports and Health Organisations
Our PWAs deliver the performance of a native app—without the app store friction. Built for speed, scalability, and usability, we craft full-stack solutions that empower users with seamless offline access, real-time updates, and device-wide compatibility.
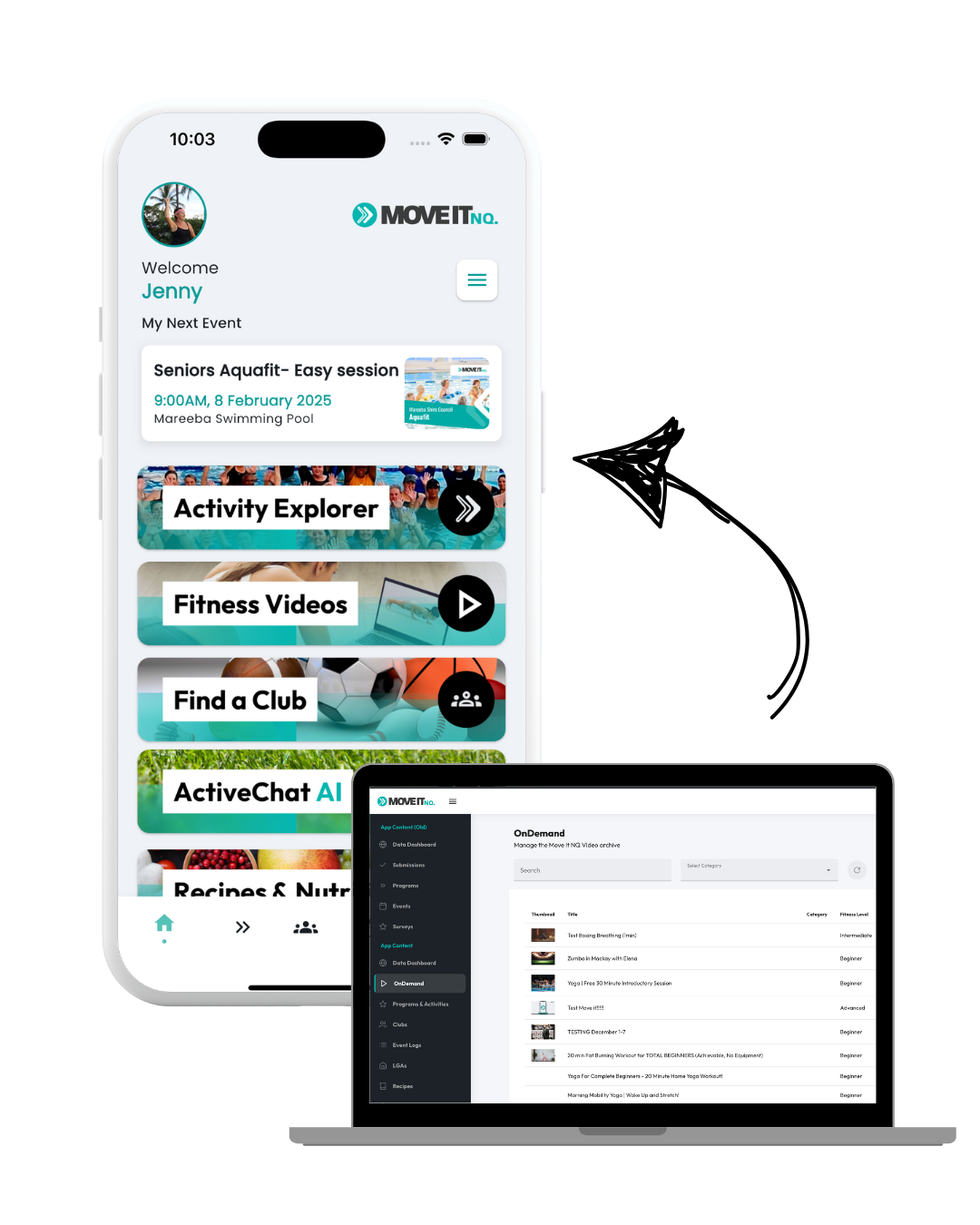
- Phone Apps without the App Store
Installable directly from your browser, our Progressive Web App (PWA) gives users a full app experience without app store gatekeeping. Fast, offline-ready, and works across all devices.
- Security & Transparency
We prioritize end-to-end encryption, secure authentication, and transparent data practices—backed by audit trails and optional blockchain verification for full trust at every layer.
- Blockchain Integrated
Our hybrid architecture connects your web experience with secure, on-chain data through blockchain integration—ideal for data ownership, digital identity, and verifiable interactions.
Our Founding Team
We’re a dynamic group of individuals who are passionate about solving problems and building a community.

Tori West
Founder & Chief Executive Officer
2024 Paris Olympian (Heptathlon) with over 10 years experience in digital development for health and sports.
TikTok 26,900Instagram 5,400
Kipling Crossing
Chief Technology Officer
10+ years in software development. Content Creator in North East India
Instagram 110,000YouTube 110,000
Sam Leslie
General Manager & Medical Lead
29+ years Sports Physiotherapist & Practice Owner. AFL Boundary Umpoire (200 games + Grand Final)